This website uses cookies. By clicking Accept, you consent to the use of cookies. Click Here to learn more about how we use cookies.
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
- Extreme Networks
- Community List
- Switching & Routing
- ExtremeSwitching (EXOS/Switch Engine)
- Abnormal high CPU utilization on stack
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
Abnormal high CPU utilization on stack
Abnormal high CPU utilization on stack
Options
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Get Direct Link
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-06-2016 05:01 PM
Hello, everybody!
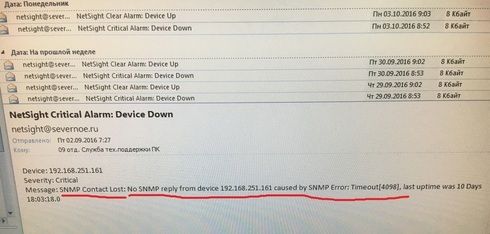
I have a stack of 2x460 and 6x440 1st generation summits (8 switches total). The problem is every morning at exactly same time I get the message from snmp (please, see the attached file).
I've noticed also, that there is constantly high CPU utilization from 20 to approximately 50% regardless of the day time. The EXOS version is 15.7.4.2.
Please, share your ideas about reasons why it happening.
Many thanks in advance,
Ilya
I have a stack of 2x460 and 6x440 1st generation summits (8 switches total). The problem is every morning at exactly same time I get the message from snmp (please, see the attached file).
I've noticed also, that there is constantly high CPU utilization from 20 to approximately 50% regardless of the day time. The EXOS version is 15.7.4.2.
Please, share your ideas about reasons why it happening.
Many thanks in advance,
Ilya
10 REPLIES 10
Options
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Get Direct Link
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-06-2016 07:14 PM
No. No NLB. In my case it is a machinecntroller from Siemens (S7), which is sending a lot of multicasts and brings CPU to 85% in average.
Options
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Get Direct Link
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-06-2016 05:28 PM
If possible you can disable all edgeports and enable them one after the other and look which port is responsible for the high cpu load.
Options
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Get Direct Link
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-06-2016 05:28 PM
you have configuring Windows NLB on the stack?
Options
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Get Direct Link
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-06-2016 05:25 PM
Lots of multicast traffic can be generated by many end systems sending some multicast, e.g. Bonjour, MDNS, LLMNR, SSDP/UPnP. These packets are sent to the switch CPU, but the switch does not use the information.
Taking a packet capture should give you information about the amount of this kind of multicast traffic in your network.
You can stop those packets from affecting the switch CPU by using an ACL. You can use the following as an example to start from:
entry deny_MDNS { if match all { destination-address 224.0.0.251/32; } then { deny-cpu; count MDNS-deny; } } entry deny_LLMNR { if match all { destination-address 224.0.0.252/32; } then { deny-cpu; count LLMNR-deny; } }The counters give you a way to see if there were packets affected by the ACL.
You might want to take a look at the GTAC Knowledge article How can I block mDNS with an ACL using MAC addresses as well.
Taking a packet capture should give you information about the amount of this kind of multicast traffic in your network.
You can stop those packets from affecting the switch CPU by using an ACL. You can use the following as an example to start from:
entry deny_MDNS { if match all { destination-address 224.0.0.251/32; } then { deny-cpu; count MDNS-deny; } } entry deny_LLMNR { if match all { destination-address 224.0.0.252/32; } then { deny-cpu; count LLMNR-deny; } }The counters give you a way to see if there were packets affected by the ACL.
You might want to take a look at the GTAC Knowledge article How can I block mDNS with an ACL using MAC addresses as well.
Options
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Get Direct Link
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-06-2016 05:25 PM
The reason for high cpu can be a device sending a lot of multicasts. Because multicasts are pricessed in the main cpu the load will inctease with the amount of multicasts being send to the device. You can figure it out by inspecting a tracefile. I have a similar issue and the only way to decrease cpu load was an accesslist which blocks multicasttraffic on the port where the sending device is attached.